1. Acne (pimples)
This is one of the most classic and effective applications of red light therapy.
Mechanism of Action: Primarily due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Red light penetrates the sebaceous glands, inhibiting the growth of inflammatory bacteria (primarily Propionibacterium acnes), while also reducing the redness, swelling, and pain of acne.
Usage: Often used in combination with blue light (primarily for antibacterial effects) for enhanced results.
2. Skin Wound Healing and Repair
Red light can significantly accelerate the healing process of various wounds.
Mechanism of Action: It stimulates fibroblasts to produce more collagen and elastin, promoting angiogenesis and thus accelerating tissue repair.
Applications:
Surgical Incisions and Wounds: Reduces scarring.
Diabetic Ulcers and Pressure Sores: An important adjunctive treatment.
Burns: Promotes wound healing and reduces scarring.
3. Skin Aging and Photoaging (Anti-Aging)
Red light therapy is often referred to as “phototherapy” in the beauty field.
Mechanism of Action: By stimulating fibroblasts, it increases collagen and elastin synthesis, thereby improving skin texture, reducing fine lines and wrinkles, increasing skin elasticity, and improving skin tone.
Effects: Studies have shown that regular use can significantly improve skin smoothness and firmness.
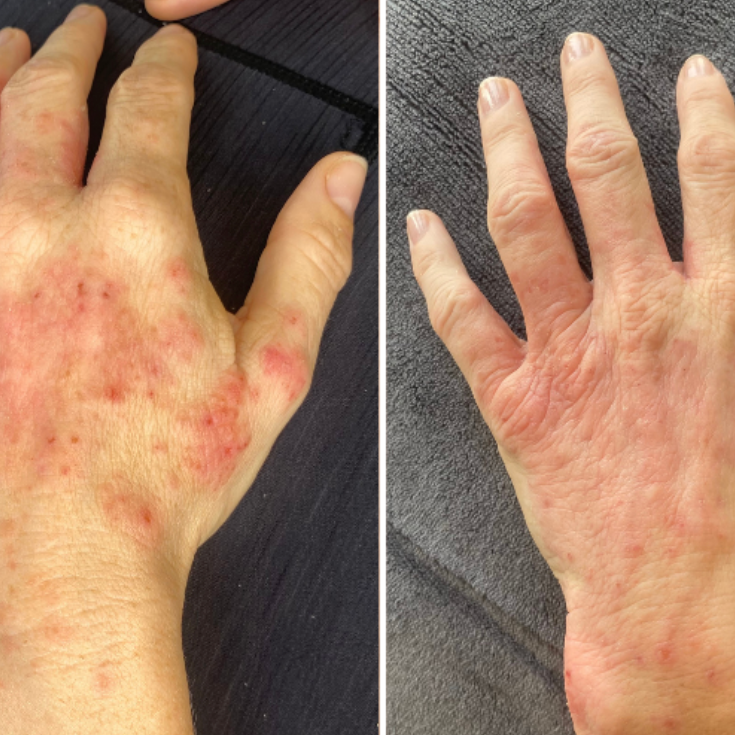
4. Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis
Mechanism of Action: Leveraging its potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, it reduces skin inflammation and itching.
Note: It is typically used as an adjunctive treatment for moderate to severe dermatitis and should be used under a doctor’s supervision.
5. Psoriasis
Mechanism of Action: It regulates abnormal proliferation and differentiation of skin cells and reduces inflammation in plaque areas.
Status: It has some efficacy, but is usually used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan rather than as a monotherapy.
6. Herpes and Shingles
Mechanism of Action: It reduces pain and inflammation and may accelerate the healing process of blisters.
Benefits: It may also have some effect on the neuralgia associated with postherpetic neuralgia.
7. Rosacea
Mechanism of Action: Helps reduce persistent facial erythema, flushing, and inflammation, especially for inflammatory papules and pustules.
Caution: Carefully control the amount of energy used to avoid excessive heat stimulation.
8. Hair Loss (Androgenic Alopecia)
Mechanism of Action: Low-intensity laser/red light is believed to stimulate energy production in hair follicle cells, prolonging the anagen phase and promoting hair growth.
Applications: Devices such as laser hair growth caps are already approved by the US FDA.
9. Pigmentary Disorders (e.g., Melasma)
Mechanism of Action: Through its anti-inflammatory effects and skin barrier repair, it can help improve some post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and melasma. However, it is usually used in combination with other treatments (e.g., hydroquinone, acid peels, etc.).
Post time: 09-28-25
